You can download the docker engine for your specific OS from the dockerDocs
Also, you can download a docker image from the dockerhub.Search for an image you want to use.
Select the appropriate tag for your image(default of images is latest).
https://hub.docker.com/
An example of an image could be nginx. the command
docker pull nginx
gets you the image with the latest tag.
The output of this image would look like above.
Now we can create a container from an image.(A container is a running instance of an image)
To run an image we can use the command
docker run nginx:latest
To check if our container is running we use the command
docker container ls
This gives list of our running images(containers)
If we check the container section of our docker machine we can see our container running
When we check our running image(container) we can see there is a default name and the time the container started.
from our bash shell you can see the container is running we can stop the container with ctl+C. This stops the container and if we check the container list(docker container ls) we can see the container nginx does not show anymore.
The run command with -d
Implies running the image in detach mode which allows it not to hang in the bash. After it starts running we can see the containner
id on the last line.

docker ps
shows us all the docker processess running. and we can see our nginx is running with tag and default generated name
Exposing Port
This allows our host to get access to docker instances in the docker machine.
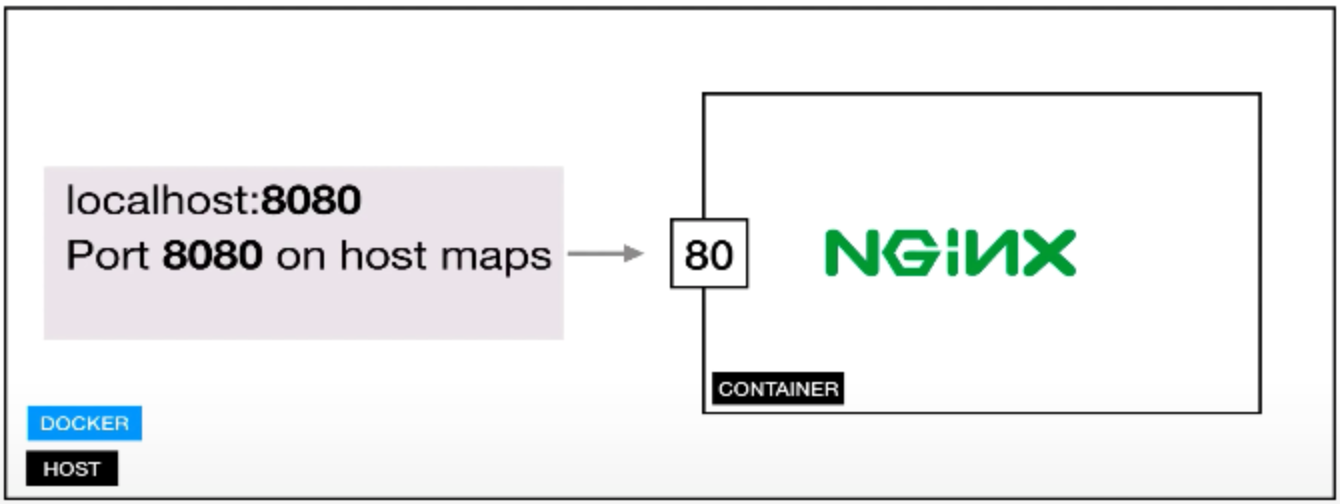
to make sure our local host can get access to the running docker instance we need to stop our instance and rerun so that our local host can access
the running container. To do that we run
to run the container to match host port we run
docker run -p 8088:80 -d nginx:latest

This runs the container and we can access the container on port 8088 on our local host machine.

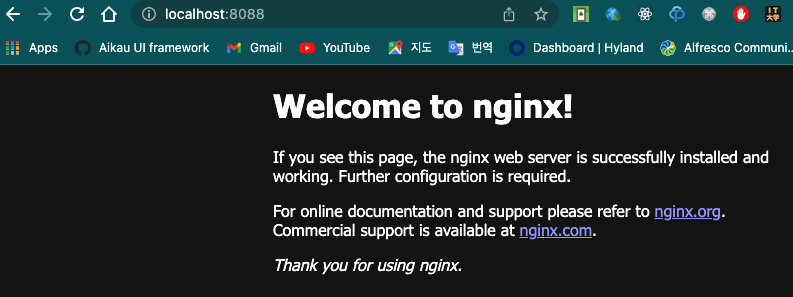
from the image we can see that our port is different. set to 8088.
we can open our browser to see that our container is running on our specified port.
we can match our docker container port to multiple ports on the local host by using -p again to specify multiple ports
docker run -p 8088:80 -p 8888:80 -d nginx:latest
accessing the localhost device browser on port 8088 or 8888 should display as before.
check the port column how multi ports were given

Managing Containers
How to stop, remove start and name containers.
Stop Container
We can stop a running container with the command
docker stop [___container_name or containerID]
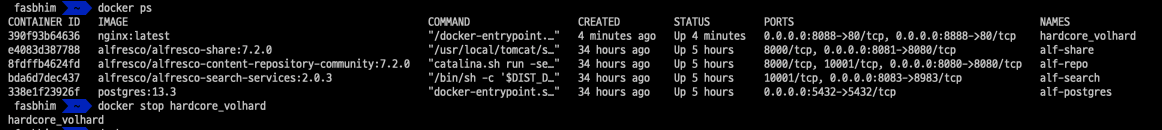
Start container
To start an existing container we can just use the container name to start the container
docker start hardcore_volhard
we have started the previous container we stopped again.
Delete container
We can also delete a container with the container id or the container name
docker rm [___container_name or containerID]
- we can also delete all docker containers
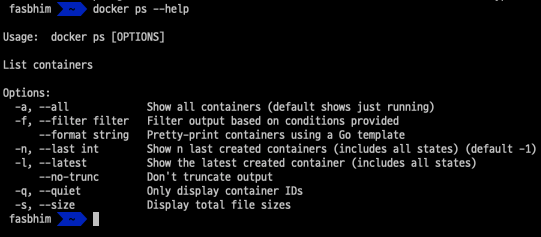
- check the docker ps options
-
we can get all docker containers which are quite(not running)
- -a, --all Show all containers (default shows just running)
- -q, --quiet Only display container IDsdocker ps -aq
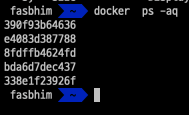
if we want to delete all these docker containers we can run
docker rm $(docker ps -aq)
to delete all the containers. NB: This command does not work for containers that are running.
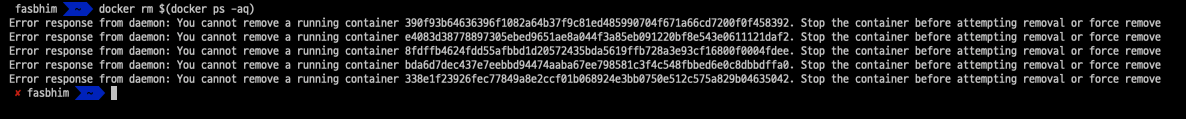
well this situation can be overridden if we want to actually delete even running containers then we need to make it force.
docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq)
-f is used to force the command deletion.
Naming Containers
Using docker assigns a random name when we do not specify a name. example is when we created nginx
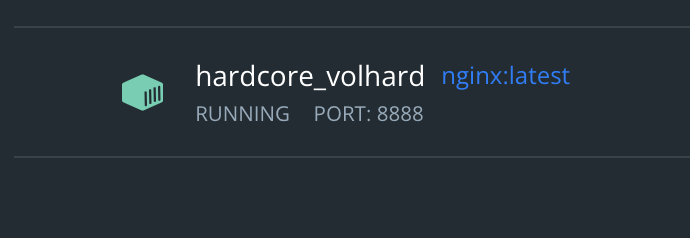
The way we give docker a name is by using --name [customName]
docker run -p 8088:80 -p 8888:80 --name customNginx -d nginx:latest
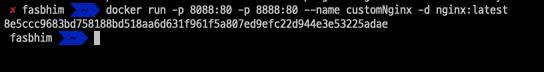
docker ps
would display our custom name given
Docker containers naming makes it easy to identify our containers and easy to manage a container.
'DevOps' 카테고리의 다른 글
| How to Enable root User Login in EC2 (0) | 2023.03.02 |
|---|---|
| onlyoffice for alfresco 7.2.X | 7.3.X (0) | 2023.01.09 |
| What is API Gateway Throttling (0) | 2022.09.28 |
| Dockerfile (0) | 2022.05.24 |
| Docker Process & Volumes (0) | 2022.05.23 |