Apache POI - the Java API for Microsoft Documents
Read and write MS Excel files using Java
read and write MS Word
MS PowerPoint files using Java
The Apache POI Project's mission is to create and maintain Java APIs for manipulating various file formats based upon the Office Open XML standards (OOXML) and Microsoft's OLE 2 Compound Document format (OLE2).Office Open XML standards (OOXML)
Microsoft's OLE 2 Compound Document format (OLE2)
OLE2 files include most Microsoft Office files such as XLS, DOC, and PPT as well as MFC serialization API based file formats
Office OpenXML Format is the new standards based XML file format found in Microsoft Office 2007 and 2008. This includes XLSX, DOCX and PPTX. The project provides a low level API to support the Open Packaging Conventions using openxml4j.
For each MS Office application there exists a component module that attempts to provide a common high level Java api to both OLE2 and OOXML document formats.
In all cases we can refer to the java documentations for the specifications.
SpreadSheet
Overview
- HSSF is the POI Project's pure Java implementation of the Excel '97(-2007) file format.
- XSSF is the POI Project's pure Java implementation of the Excel 2007 OOXML (.xlsx) file format.
HSSF and XSSF provides ways to read spreadsheets create, modify, read and write XLS spreadsheets.
They provide: - low level structures for those with special needs
- an eventmodel api for efficient read-only access
- a full usermodel api for creating, reading and modifying XLS files
NB: merely reading spreadsheet data, then use the eventmodel api in either the org.apache.poi.hssf.eventusermodel package, or the org.apache.poi.xssf.eventusermodel package, depending on your file format.
Also , the new XSSF supported Excel 2007 OOXML (.xlsx) files are XML based, the memory footprint for processing them is higher than for the older HSSF supported (.xls) binary files.
Quick Guide
In this examples for developers guide i would create simple springboot application to test the various service/event apis.
Optional:(Include lombok and spring web)
In our maven pom.xml file we need the old and the new poi dependencies(just to test both features).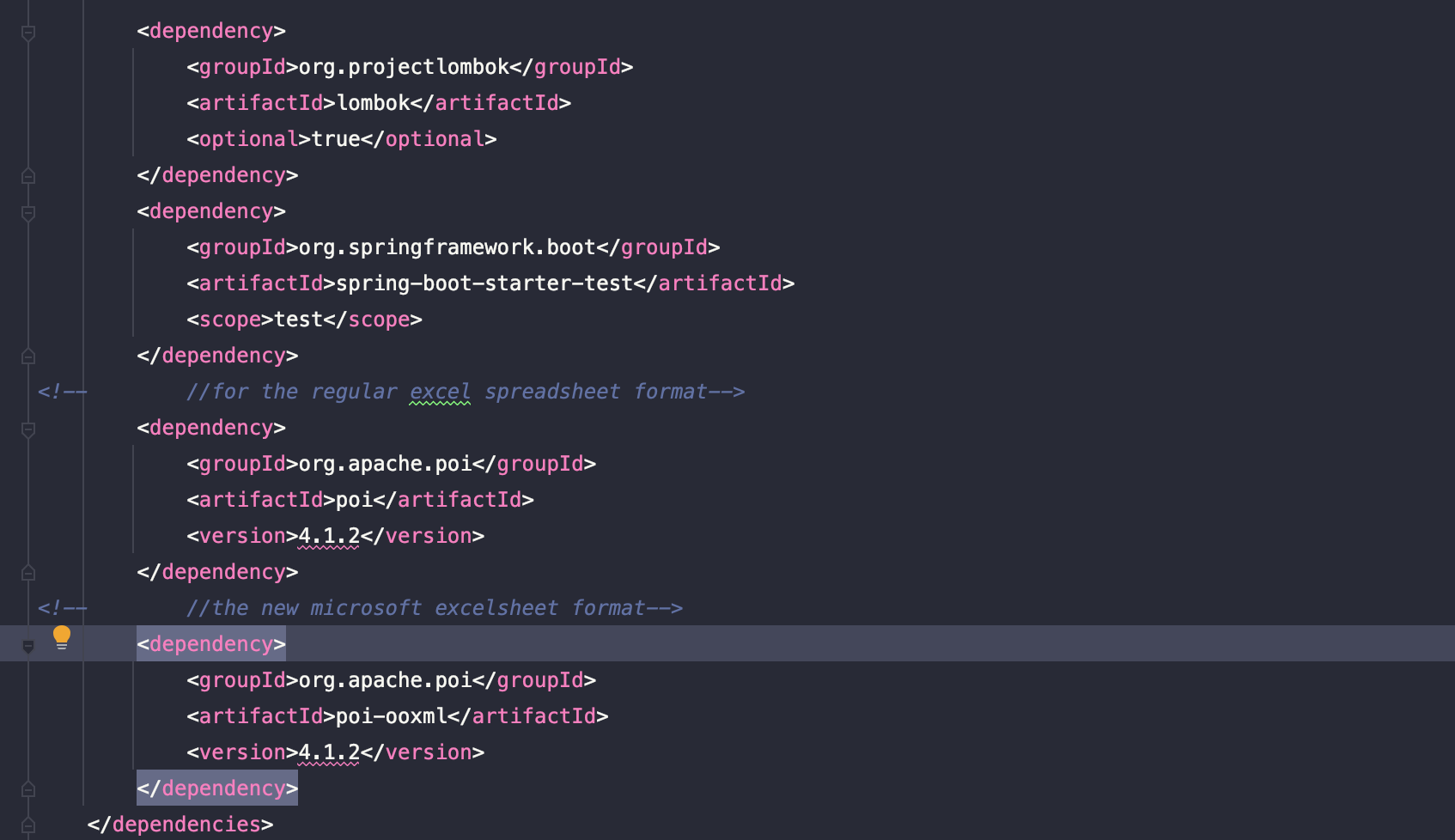
Application Apis
How to create a new workbook
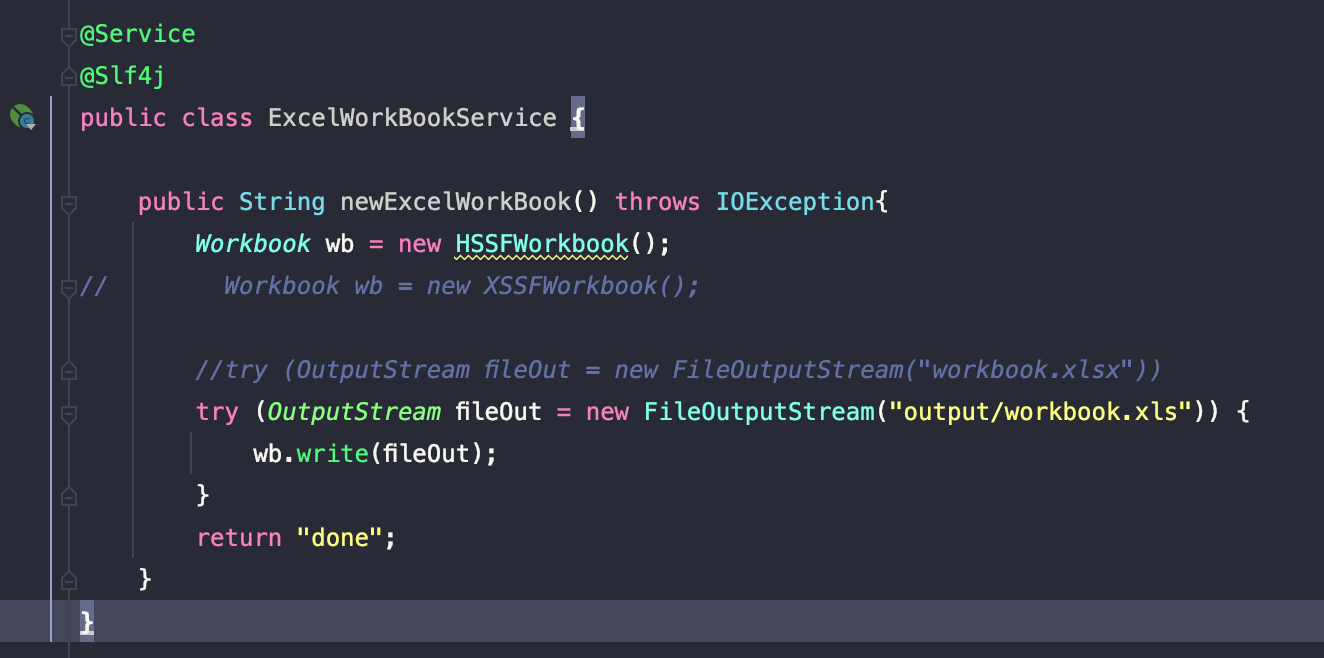
When we run the test code. We can see in our output directory the file workbook.xls created.
class ExcelWorkBookServiceTest {
@Test
public void testWorkBookCreation() throws IOException{
System.out.println(new ExcelWorkBookService().newExcelWorkBook());
}
}How to create a sheet
We can create sheets and embedded them into our excel workbook and this simple method does that.
private void newSheetsCreations(Workbook wb) {
Sheet sheet1 = wb.createSheet("Fasnew sheet");
Sheet sheet2 = wb.createSheet("Fas Data sheet");
String safeName = WorkbookUtil.createSafeSheetName("[O'Stocks's sales*?]"); // returns " O'Stocks's sales "
Sheet sheet3 = wb.createSheet(safeName);
}When we observe the previous workbook we can see the sheets created.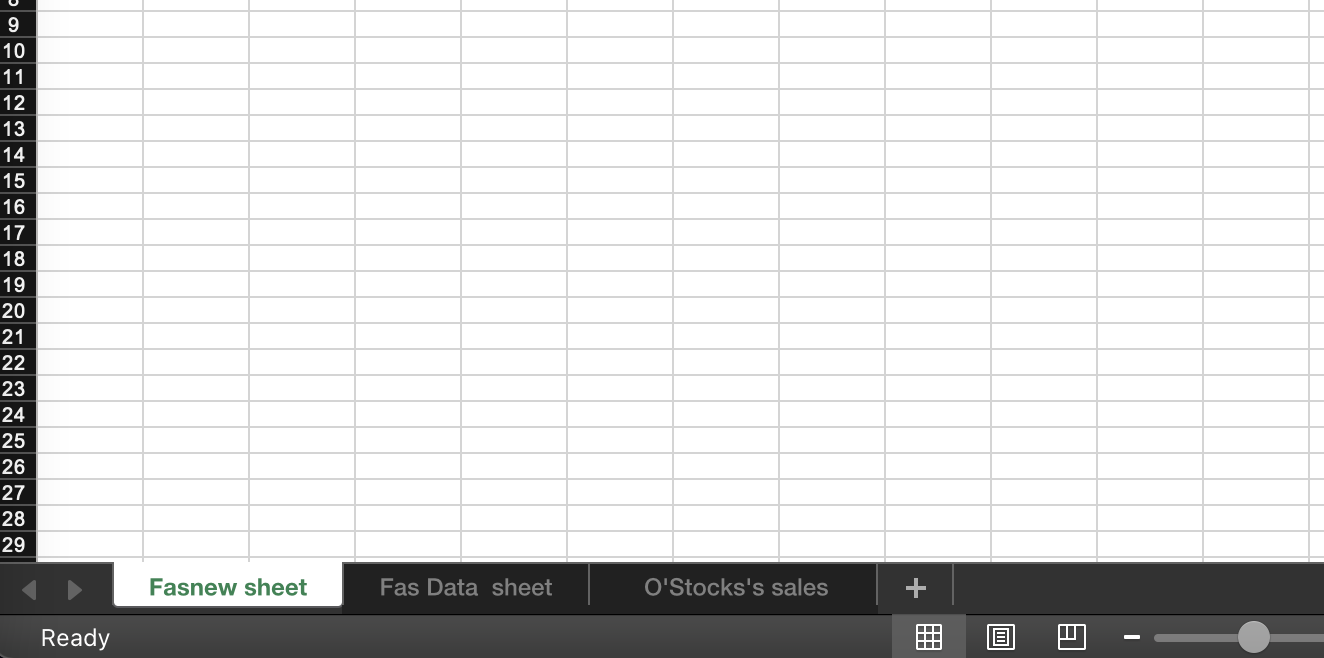
How to create cells
We add some new cells and rows to the sheet(Fasnew sheet).And the CreationHelper to create text.
private void creatingCells(Workbook wb, Sheet sheet1) {
CreationHelper createHelper = wb.getCreationHelper();
// Create a row and put some cells in it. Rows are 0 based.
Row row = sheet1.createRow(0);
// Create a cell and put a value in it.
Cell cell = row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellValue(1);
// Or do it on one line.
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(1.2);
row.createCell(2).setCellValue(createHelper.createRichTextString("This is a string"));
row.createCell(3).setCellValue(true);
}we would run the test code to see the new content in sheet1
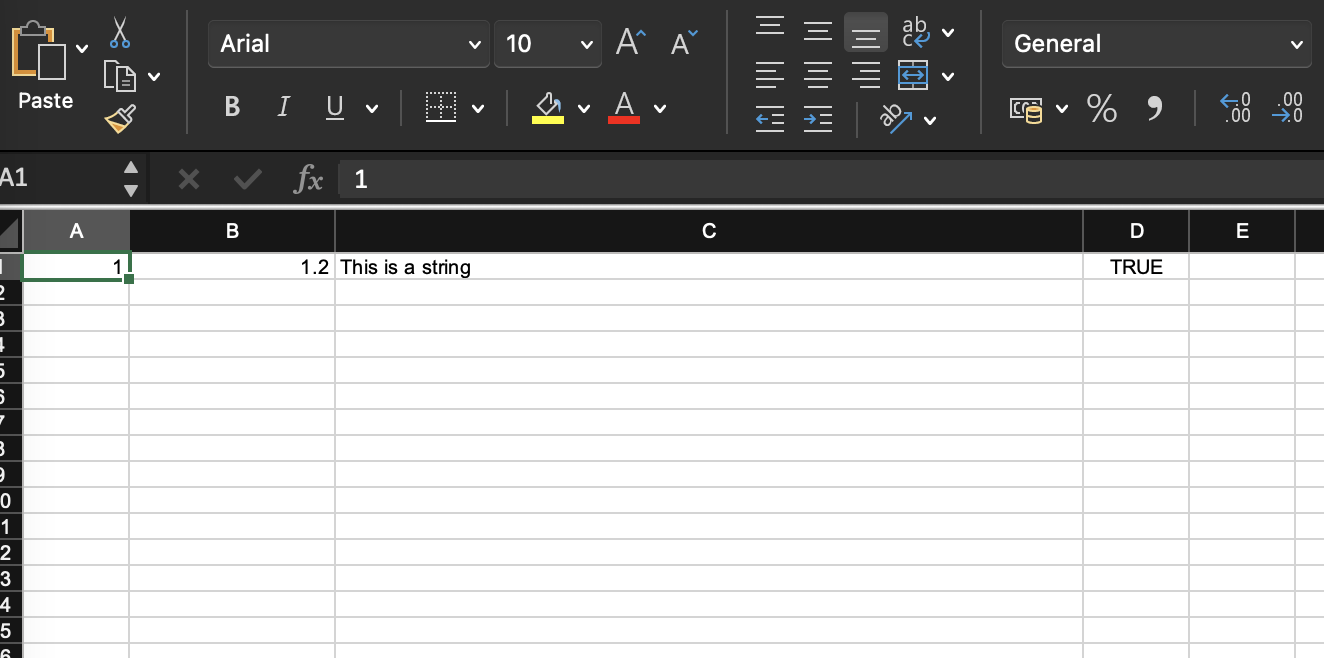
How to create date cells
We can also create a date cell.
NB: Observe how the rows and cells has integer values. They indicate the location of the row or cell on the excel file.
if we wish to write more data, we need to increment the location to suit our prefered location of writing.
private void creatingDateCell(Workbook wb, Sheet sheet1, CreationHelper createHelper) {
Row row = sheet1.createRow(0);
Cell cell = row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellValue(new Date());
CellStyle cellStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
cellStyle.setDataFormat(createHelper.createDataFormat().getFormat("m/d/yy h:mm"));
cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue(new Date());
cell.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
//you can also set date as java.util.Calendar
cell = row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue(Calendar.getInstance());
cell.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
}different cells
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
Row row = sheet.createRow(2);
row.createCell(0).setCellValue(1.1);
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(new Date());
row.createCell(2).setCellValue(Calendar.getInstance());
row.createCell(3).setCellValue("a string");
row.createCell(4).setCellValue(true);
row.createCell(5).setCellType(CellType.ERROR);
// Write the output to a file
try (OutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls")) {
wb.write(fileOut);
}Files vs InputStreams
When opening a workbook, either a .xls HSSFWorkbook, or a .xlsx XSSFWorkbook, the Workbook can be loaded from either a File or an InputStream. Using a File object allows for lower memory consumption, while an InputStream requires more memory as it has to buffer the whole file.
We can generalize our code from start to make late output much flexible by using the WorkBookFactory.
// Use a file
Workbook wb = WorkbookFactory.create(new File("MyExcel.xls"));
// Use an InputStream, needs more memory
Workbook wb = WorkbookFactory.create(new FileInputStream("MyExcel.xlsx"));NB: If using HSSFWorkbook or XSSFWorkbook directly, you should generally go through POIFSFileSystem or OPCPackage, to have full control of the lifecycle (including closing the file when done):
// HSSFWorkbook, File
POIFSFileSystem fs = new POIFSFileSystem(new File("file.xls"));
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fs.getRoot(), true);
....
fs.close();
// HSSFWorkbook, InputStream, needs more memory
POIFSFileSystem fs = new POIFSFileSystem(myInputStream);
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fs.getRoot(), true);
// XSSFWorkbook, File
OPCPackage pkg = OPCPackage.open(new File("file.xlsx"));
XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(pkg);
....
pkg.close();
// XSSFWorkbook, InputStream, needs more memory
OPCPackage pkg = OPCPackage.open(myInputStream);
XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(pkg);
....
pkg.close();
Alignment options
creatingCells(wb, row, 0, HorizontalAlignment.CENTER, VerticalAlignment.BOTTOM);
creatingCells(wb, row, 1, HorizontalAlignment.CENTER_SELECTION, VerticalAlignment.BOTTOM);
creatingCells(wb, row, 2, HorizontalAlignment.FILL, VerticalAlignment.CENTER);
creatingCells(wb, row, 3, HorizontalAlignment.GENERAL, VerticalAlignment.CENTER);
creatingCells(wb, row, 4, HorizontalAlignment.JUSTIFY, VerticalAlignment.JUSTIFY);
creatingCells(wb, row, 5, HorizontalAlignment.LEFT, VerticalAlignment.TOP);
creatingCells(wb, row, 6, HorizontalAlignment.RIGHT, VerticalAlignment.TOP);Working with borders
private void creatingBorders(Workbook wb, Cell cell) {
// Create a cell and put a value in it.
cell.setCellValue(4);
// Style the cell with borders all around.
CellStyle style = wb.createCellStyle();
style.setBorderBottom(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setBottomBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex());
style.setBorderLeft(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setLeftBorderColor(IndexedColors.GREEN.getIndex());
style.setBorderRight(BorderStyle.THIN);
style.setRightBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLUE.getIndex());
style.setBorderTop(BorderStyle.MEDIUM_DASHED);
style.setTopBorderColor(IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex());
cell.setCellStyle(style);
}Getting the cell contents with Control of missiong content
// Decide which rows to process
int rowStart = Math.min(15, sheet.getFirstRowNum());
int rowEnd = Math.max(1400, sheet.getLastRowNum());
for (int rowNum = rowStart; rowNum < rowEnd; rowNum++) {
Row r = sheet.getRow(rowNum);
if (r == null) {
// This whole row is empty
// Handle it as needed
continue;
}
int lastColumn = Math.max(r.getLastCellNum(), MY_MINIMUM_COLUMN_COUNT);
for (int cn = 0; cn < lastColumn; cn++) {
Cell c = r.getCell(cn, Row.RETURN_BLANK_AS_NULL);
if (c == null) {
// The spreadsheet is empty in this cell
} else {
// Do something useful with the cell's contents
}
}
}
Text Extraction
Text extraction provided by standard ExcelExtractor class.
try (InputStream inp = new FileInputStream("workbook.xls")) {
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(new POIFSFileSystem(inp));
ExcelExtractor extractor = new ExcelExtractor(wb);
extractor.setFormulasNotResults(true);
extractor.setIncludeSheetNames(false);
String text = extractor.getText();
wb.close();
}There are several applications of the apache poi. It provides many services which is not included in this. refer to the docs for more.
A continuation would be on working with word files.
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| MANUAL INSTALLATION of ACS-7.2.0, ASS-2.x and Local T-Engine Service using distribution package (0) | 2023.02.28 |
|---|---|
| What is Singleton Design Pattern? (0) | 2022.11.10 |
| HashMap Sorting Errors [Entry Result Manipulations]. (0) | 2022.09.18 |